Enterprise network infrastructures are under increasing pressure as requirements build. The sheer number and diversity of connected devices and systems are exploding. Network convergence—IT/OT, power/data—is ramping up. At the same time, more resources are being pushed to the edge, extending the network further and further.
Now, more than ever, having an infrastructure platform that can efficiently address these challenges, as well as future ones, is critical. The scope and complexity of the connected enterprise network will only continue to expand. There’s a lot riding on your platform selection.
At CommScope, we know a thing or two about network change, and the importance of getting it right. Our 40+ years of enterprise experience and understanding of where the technology is heading all point to the same conclusion: Category 6A cabling and connectivity. Full stop.
On this resource page, we lay out the trends, facts, and rationales behind our firm belief that Cat 6A will be the predominant enabler of tomorrow’s more connected and capable enterprise network.
Read through our summaries, download our resources, learn with our tools, and watch videos to explore the next sections.
Rear side of a rack equipped with Cat 6A cabling

The evolution of Category cabling and the future of tomorrow’s network
We invite you to examine the evidence, then draw your own conclusions. First introduced by CommScope, as SYSTIMAX® GigaSPEED® X10D, in 2004 and standardized in 2009, Category 6A remains the recommended infrastructure for modern new builds. So how did we get here?
In 2004, the industry recognized the bandwidth limitations of Category 5 and Category 6 cabling categories would severely constrain network growth and development. A major challenge was supporting higher data rates over longer distances, compared to Category 6.
Led by the IEEE 802.3an 10GBASE-T Task Force, the search for a 10 GE-capable solution was on. They began by tackling fundamental issues like return loss, crosstalk, and noise from adjacent cabling channels (alien crosstalk). Their work resulted in minimum cabling channel specifications for 10GBASE-T and a new class of cabling, Class EA, otherwise known as “Augmented” Category 6. In October 2004 Cat 6A was officially born.
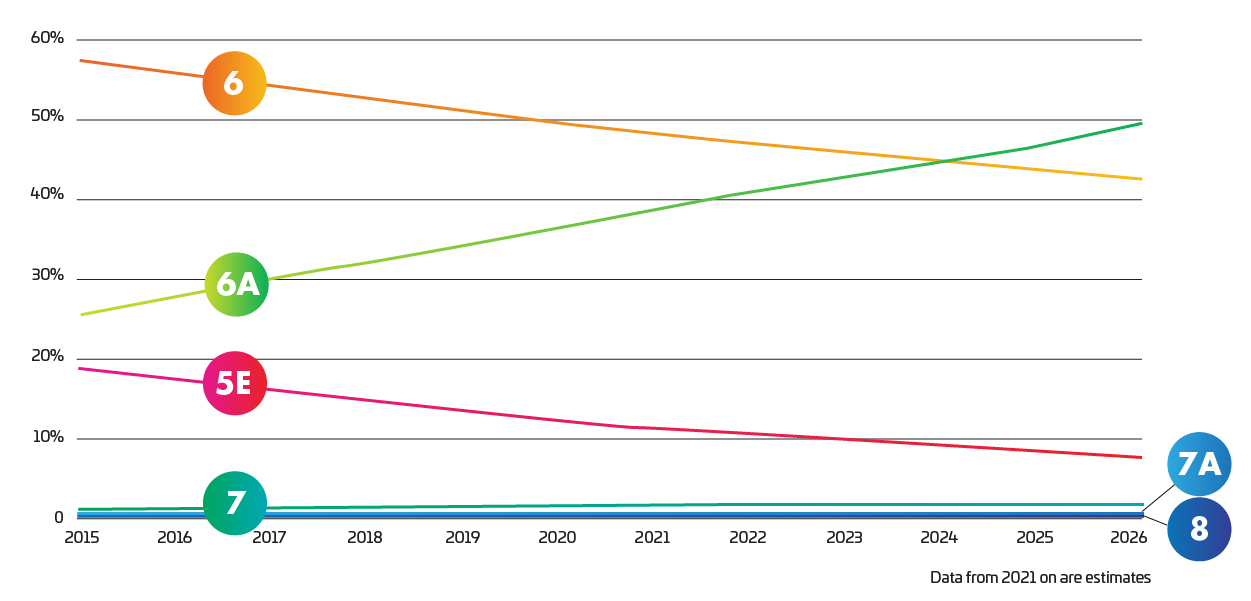
As new applications require better cable performance, adoption rates of Cat 6A have steadily increased. Drivers such as IoT, Wi-Fi 6/6E/7, four-pair PoE, smart lighting, building control/automation, in-building cellular, and more, will extend the uptake of Category 6A for the foreseeable future.
Based on the graph, looks like the smart money is on Category 6A.
Marketshare % by category

CAT 6A: Hard facts
Network speed vs span: How fast depends on how far
Much of the network’s design depends on where the data is generated and where it must be processed and stored. More network resources are moving to the edge while data speeds and capacity demands keep increasing beyond the capabilities of existing Category 5 and Category 6 networks.
Specifically, Category 5/6 are susceptible to channel impairments created inside the operating environment. Crosstalk, impedance mismatch, external noise, return loss, and other issues cause bit errors that can reduce overall throughput. Category 6A cabling is specifically engineered to overcome these challenges, enabling networks to support 10 GE channels up to 100 meters—nearly three times longer than Category 6.
Not just any Cat 6A. CommScope’s family of Category 6A solutions provides enhanced cable and connector performance, so you can support the latest 10 GbE requirements.
Supported distance (m) per application and cabling category
+per+application+and+cabling+category/Zz0zM2JlMjE4MjNiZDgxMWYwYjBhM2QyZTRhMDdlYjlkYg==)
| Category | Bandwidth | Distance for 1G | Distance for 10G |
| Cat 5e | 100 MHz | 100m | _ |
| Cat 6 | 250 MHz | 100m | 37m |
| Cat 6A | 500 MHz | 100m | 100m |
| Cat 7 | 600 MHz | 100m | 100m |
| Cat 7A | 1000 MHz | 100m | 100m |
| Cat 8 | 2000 MHz | 100m | 100m |
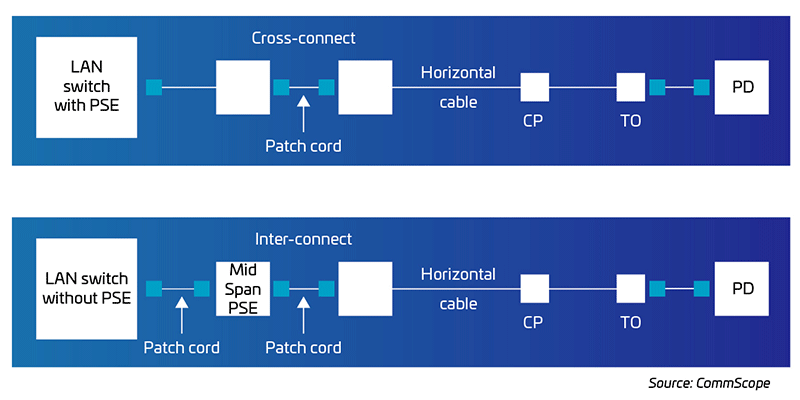
Meeting PoE power standards for connected devices
Full-on network convergence in the enterprise space is underway. Device OEMs are taking advantage of updated PoE standards that enable all four cable pairs to double the power delivery compared to PoE applications using just two pairs. For applications requiring more than 25.5 watts, the only standards-recommended cabling solution is, you guessed it, Cat 6A.
Power from LAN equipment with end-span PSE (top) and a mid-span (bottom)
To learn more about PoE and the standards guiding its development, check out Power Over Ethernet: Topics and Technologies.
Standardized Support for Cat 6A
Since its introduction, Category 6A has been recommended by industry standards organizations around the world for a wide range of applications. The following are just a few examples:
Defining Category 6A:
Ratified in 2004, IEEE 802.3an-2006 10GBASE-T specified Cat 6A for repeatable alien crosstalk performance in 500 MHz applications, citing Cat 6A’s improved insertion loss versus Cat 6.
General in-building cabling:
In February 2008, the ISO adopted amendments to the global ISO/IEC 11801 standard, providing for a link/channel up to 500 MHz using Cat 6A cable/connectors.
Power over Ethernet:
TIA’s TSB-184-A Guidelines for Supporting Power Delivery Over Balanced Twisted-Pair Cabling recommends Cat 6A cabling to better support IEEE 802.3bt four-pair PoE.
Wireless access points:
TIA’s TSB-162-A Telecommunications Cabling Guidelines for Wireless Access Points recommends Cat 6A for horizontal cabling to WAPs in new installations.
Healthcare facilities: ANSI/TIA-1179-A Healthcare Facility Telecommunications Infrastructure Standard. Cat 6A is recommended for new installations (for both backbone and horizontal copper cabling).
Our top ten reasons for choosing Category 6A
Based on what you’ve read thus far, we suspect you’ll agree the use case for Cat 6A is pretty strong (and even more so for CommScope Cat 6A).
In this infographic, we count down our Top 10 reasons for choosing the technology. Got a favorite that didn’t make our list? We’d love to hear it. Send us your suggestions at GlobalEnterpriseMarketing@commscope.com.

Ready for a Cat 6A deep technical dive?
Ready for a Cat 6A deep technical dive? Until now, we’ve been skimming the surface of a very deep and expansive topic. If you’re game, we invite you into the deep end to explore the various applications, developments and performance benefits of Cat 6A in greater detail.
Watch our short video on the science of Cat 6A and what makes it physically and electrically different from Cat 5 and Cat 6.
Want to go even deeper in market trends, the growth of Cat 6A applications, the evolution of Cat 6A standards, the global uptake of the technology, and its other fascinating aspects? We lay it all out for you here in CommScope’s Cat 6A structured cabling fact file. Your cabling infrastructure is both the nervous and circulatory system of your enterprise building and campus network. Its function is to transport the data and power that support an increasingly hyperconnected ecosystem.
Your enterprise cabling must evolve to meet the rising demands of more performance-intensive applications—and Cat 6A cabling gives you the best chance of success. By providing a long-term platform that can support multiple technology migrations, Cat 6A helps you realize more value from your entire enterprise network investment.
Explore our Category Choosing Tool
Cat 6A is a robust, future-ready cabling platform—not a panacea. But is it the best choice in every situation? That depends. Based on the circumstances, some use cases may be better suited to Cat 6 or Cat 5e. So, how do you know?
CommScope has developed a handy Category Choosing Tool to help guide you in selecting the right technology based on your specific application, environment and requirements.

CAT 6A frequently asked questions
Although deployment of Category 6A has been steadily increasing since 2004, there are still questions and misconceptions regarding what it can and can’t do. The following are some of the most frequently asked questions and answers—directly from the source.
Got additional questions? We’re happy to help. Shoot us an email.
Category 6A vs other Category cabling FAQs
-
Cat 6 has been around longer than Cat 6A. Also, some customers are not yet ready to deploy 10 GE, Wi-Fi 7 or PoE++. However, we believe cabling decisions should be made with a long-range view, at least 20 years, to avoid unforeseen costs and challenges. Cat 6A is far more future-ready. BSRIA predicts that, by 2023/2024, Cat 6A will have overtaken Cat 6 in terms of market share.
- There are minimal differences in performance. Both support 10 GE over a 100 m channel. Cat 6A has a maximum frequency of 500 MHz compared top Cat 7’s 600 MHz. The difference is that Cat 7 requires non-RJ45 connectors and heavy shielding (that needs to be grounded to work properly). So, deploying Cat 7 (and 7A) may be more expensive without any significant performance improvements.
- Cat 8 was designed for data center connectivity at 40 gig or higher. At those speeds, the conversation shifts to fiber—especially for switch-to-switch data center connections. That’s why Cat 8 was designed for just two connections and just up to 30 m.
- NBaseT can support 2.5G over Cat 5e—or 5G over Cat 6. For higher speeds, there is no better option than Cat 6A. For greenfield installations, even if you’re initially using NBaseT, Cat 6A provides additional bandwidth for future growth.
- As far as we know, manufacturers aren’t planning to phase out Cat 5e. However, devices requiring Cat cabling have power and bandwidth demands that Cat 5e can’t support. Such limitations should be considered when developing your infrastructure roadmap for device connectivity.
Cat 6A and power over Ethernet (PoE) FAQs
- Heat buildup and fire potential are due in part to the heat rise in the individual conductors. The smaller the gauge, the greater the heat rise. A Cat 5 cable carrying a 400 mA current exhibits a ≈10°C temperature increase, whereas that same current in a Cat 6A cable results in a 6°C rise. Heat buildup also depends on how many cables are in the bundle. There are deployment strategies you can use to help mitigate that.
- Not greatly. The heat load mainly impacts the bundled cables due to their length and density. The racks are designed to provide good air flow and heat dissipation. So, the impact inside the cabinets is negligible.
- Yes and no. Power transmission will not be affected but data transmission will. To prevent that, we recommend consulting our PoE implementation guide.
- Without a flame, it’s extremely unlikely. Bundled cables heat up but nowhere near the levels needed to become a fire hazard. The impact of the thermal load is limited to electrical performance.
Support of wireless applications FAQs
- Remember, you’re transmitting both power and data. While one Cat 6A cable can deliver 90 W to a single WAP power port, on the data side, Wi-Fi 6/6E/7 are pushing the 10 Gb boundary for WAP uplink. The bandwidth requirements will continue to grow as in-building wireless capabilities develop. Hence, the need for two connections per drop.
- 5G Indoor cellular systems (DAS or small cells) would be another good example.
Cat 6A products and distance FAQs
- All structured cabling standards, including those for Cat 6A, set a maximum length channel of 100 m (305 ft). This standardizes the support for multiple applications at any information outlet (service-area jack), providing an apples-to-apples comparison.
- Most vendors do offer thinner 6A cables/patch cords, but they are specified for shorter lengths based on the use case. We recommend consulting the vendor specifications before you decide which gauge to use.
- It depends on the 6A solution type. For a UTP system, no grounding is needed at all. For a shielded system, most (if not all) standards recommend grounding at both ends of each cable to prevent introducing additional noise. Best practice is to consult the vendors’ specifications, local codes and applicable standards.
Other questions
- Yes, ISO/IEC 11801.5 (data centers) and 11801.6 (distributed building services) both request using Cat 6A cable tested to Class EA channel performance.
- Many standards strongly recommend Cat 6A as the default cabling such as: Intelligent Buildings: TIA-862-B, Wireless Access Point: TSB-162-B, Data Centers: TIA-942-B, Healthcare facilities: TIA-1179, Education facilities: TIA-4966, Power over Ethernet (PoE): TIA TSB-184-A, ICT Design for Intelligent Buildings: ANSI/BICSI 007-2017.
- Cat 6A has a longer life cycle than Cat 5 or Cat 6. Its ability to support multiple generations of bandwidth growth and power requirements reduces product turnover and the associated impacts on the environment. Thus, it is both financially and ecologically more sustainable than Cat 5 or Cat 6.
- Overall, copper deployments in the data center have decreased considerably, but it is still used for out-of-band (OOB) connectivity. The TIA-942B standard recommends Cat 6A cabling for OOB connections.
- Applications like HDBase-T, which require transmission of high-definition video, recommend Cat 6A cabling.
-
Refer to the applications section of the Cat 6A Fact File for more information.
- Currently, all applicable standards specify a maximum channel length of 100 m (305 ft).
Questions about what Cat 6A can do?

Why CommScope CAT 6A?
Let’s talk CommScope Cat 6A
Until now, we’ve mentioned CommScope’s 6A several times but haven’t given you much detail. Let’s remedy that. After all, there are some significant differences between our Cat 6A portfolios (SYSTIMAX®, Uniprise® and NETCONNECT®) and any other Cat 6A family.
We’ve already hit the top 10 reasons to choose Cat 6A cabling. Now here are some great reasons to make sure it’s CommScope.
Brand advantages
Solution advantages
Performance edge
- From the first, and largest Cat 6A provider
- Consistent quality across 150+ countries
- Worldwide manufacturing
- Global tech support
- Single-source simplicity
- End-to-end solution: cables, patch cords, connectors, outlets, panels
- Shielded/unshielded, various fire ratings and connectors, plenum/non-plenum, low smoke zero halogen and more
- Easy design and deployment
- Time-tested, proven reliability
- Multiple panel footprints
- Preterminated options
- AIM-enabled intelligent management
- Enhanced cable/connector design supports latest 10 GbE requirements
- Best-in-class insertion loss, crosstalk
- Exceeds current ISO/IEC Class EA specification
- Performance beyond standards
CommScope Cat 6A: Sustainable, for your business and the environment
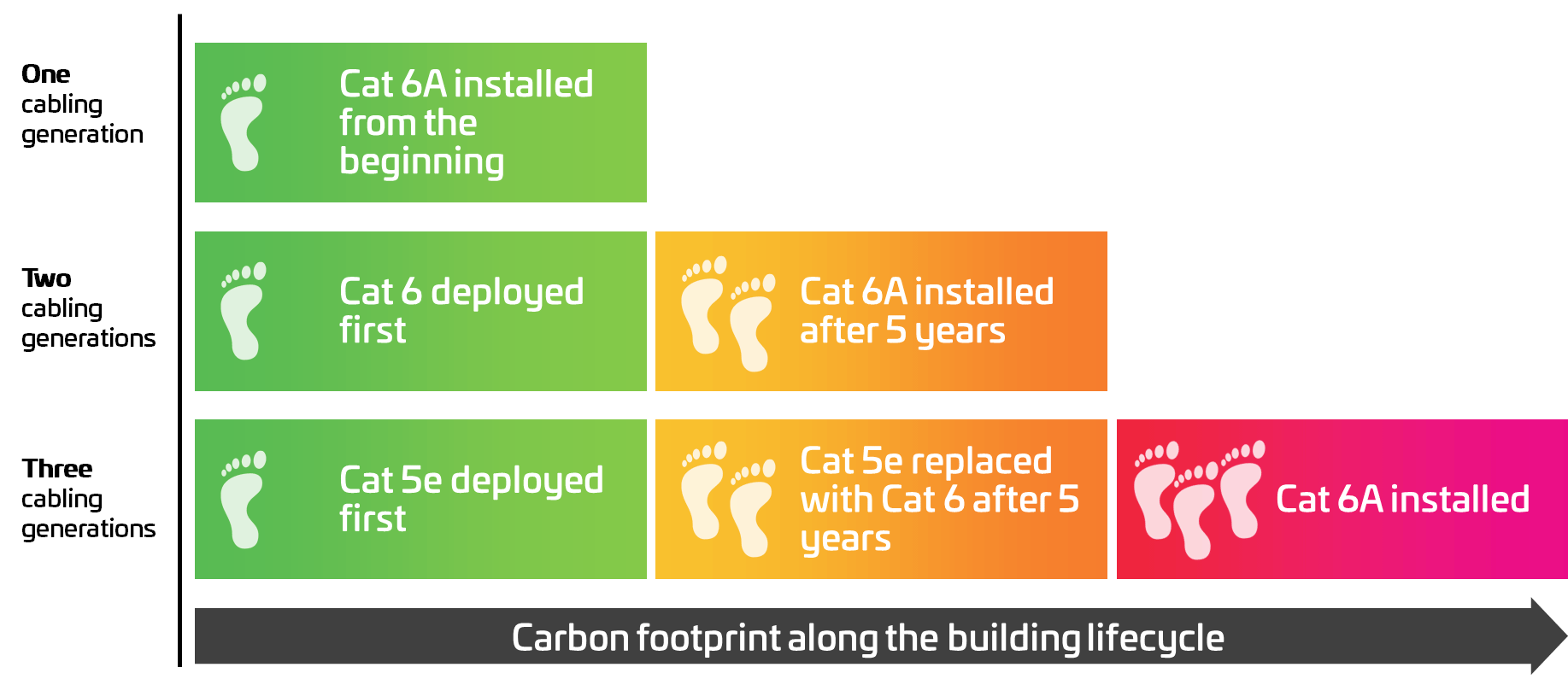
A key challenge in reducing the carbon footprint within the enterprise network is product longevity. Deploying the most current and future-ready technologies enables network managers to extend the service life of their network infrastructure and lower their carbon footprint. A benefit that snowballs across the supply chain. This is a powerful, though under-reported, strength of Cat 6A. By supporting multiple generations of bandwidth growth and power requirements, Cat 6A provides staying power that is both financially and environmentally more sustainable than Cat 5 or Cat 6.
Additionally, Cat 6A’s extended longevity also allows networks to use the same cabling network to support new generations of more energy-efficient switches, enabling lower energy usage over time.
Did you know?
Using Category 6A/OM5 technologies can lower the environmental impact 300% in 15 years.
Environmental impact after 15 years, depending on the number of cabling generations
Podcast: Drilling down on Category 6A
In this podcast, CommScope Enterprise Strategy Solutions Architect Jason Bautista takes you on a deeper dive into the benefits and staying power of Category 6A cabling. Speaking with the editors of Cabling Installation & Maintenance, Jason discusses Cat 6A’s device compatibility, current and future use cases, and more.

Summary
To steal an anatomical analogy, your cabling infrastructure is both the nervous and circulatory system of your enterprise building and campus network. Its function is to transport the data and power that nourish an increasingly hyperconnected ecosystem.
Just as your body’s blood vessels must adapt to handle increases in stress and natural aging, so, too, your enterprise cabling must evolve to meet the rising demands of more performance-intensive applications. We believe the demonstrations show Cat 6A cabling gives you the best chance of success. By providing a long-term platform that can support multiple technology migrations, Cat 6A helps you realize more value from your entire enterprise network investment.
With CommScope as your infrastructure partner, you can optimize the power of Cat 6A. Our SYSTIMAX, Uniprise and NETCONNECT Cat 6A portfolios ensure the product performance, technical support and global availability you need—wherever you need it.
To learn more about our Cat 6A offerings, or to get started, contact your CommScope representative.
“I didn’t know Cat 6A did all that!”
Looking for a few conversation starters to use at your next office party? Try some of these few fun facts about Cat 6A and amaze your friends.
Additional Resources and Case Studies

Cat 6A helps Stade de France® strengthen its reputation as Paris’s premier live entertainment destination

How Cat 6A enabled Zhongshan Securities to transform its network effectiveness

Melbourne Airport soars to new heights with Cat 6A

Why Samsung India owes some of its competitive edge to Cat 6A

How Dallas Cowboys created unique user experience with Cat 6Aat new headquarters
Structured cabling systems ordering guides
Download the ordering guide for your region:
SYSTIMAX: North America | Europe, Middle East & Africa | Asia Pacific | Caribbean & Latin America
NETCONNECT: Europe, Middle East & Africa | Asia Pacific | Caribbean & Latin America
Uniprise: North America
CommScope provides online training materials to help users develop a thorough understanding of both standards-based design using SYSTIMAX, and how it can be implemented in an ‘intelligent building’ context.

SYSTIMAX Design & Engineering